Anxiety
Introduction to Anxiety
Anxiety is a natural response to stress, characterized by feelings of worry, nervousness, or fear about future events or uncertain outcomes. While occasional anxiety is a normal part of life, chronic or excessive anxiety can interfere with daily activities and well-being. Anxiety disorders are among the most common mental health conditions, affecting millions of people worldwide, including children!

Symptoms of Anxiety
Anxiety can manifest in a variety of physical, emotional, and behavioral symptoms. Recognizing these symptoms is the first step toward seeking help and finding effective treatment. Common symptoms of anxiety include:
Physical Symptoms:
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations
- Shortness of breath
- Sweating
- Nausea or stomach problems
- Headaches or dizziness
- Muscle tension or aches
Emotional Symptoms:
- Persistent worry or fear
- Feeling restless or on edge
- Irritability
- Difficulty concentrating
- Feeling overwhelmed or out of control
- Perfectionism
Behavioral Symptoms:
- Avoidance of situations that trigger anxiety
- School avoidance and/or truancy
- Compulsive behaviors or rituals (in the case of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder)
- Social withdrawal or isolation
- Difficulty completing everyday tasks
Common Anxiety Disorders
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Characterized by excessive, uncontrollable worry about various aspects of life, such as health, work, or relationships.
- Panic Disorder: Involves recurrent, unexpected panic attacks and persistent fear of future attacks.
- Social Anxiety Disorder: Intense fear of social situations where one might be judged, embarrassed, or scrutinized by others.
- Specific Phobias: Irrational fear and avoidance of specific objects or situations, such as heights, animals, or flying.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): Involves unwanted, intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors or mental acts (compulsions) aimed at reducing anxiety.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Anxiety and flashbacks triggered by a traumatic event.
Treatment of Anxiety
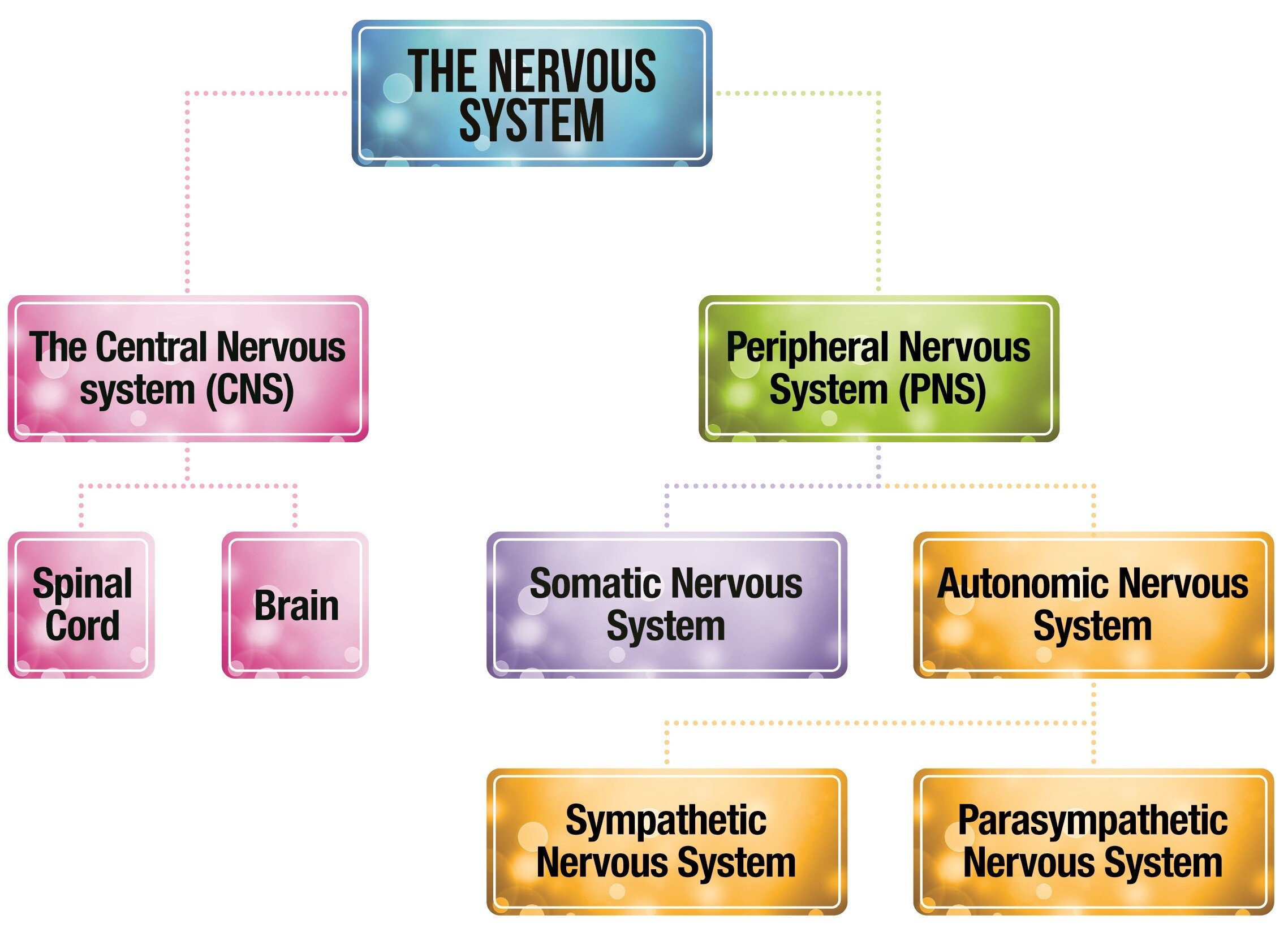
We use science! Effective treatment for anxiety often involves a combination of therapeutic approaches to decrease the stress response from the autonomic nervous system while stimulating the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for our body’s rest and digest function. Here are some common treatment options:
Therapy:
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): A structured, time-limited therapy that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to anxiety.
- Exposure Therapy: A form of CBT that gradually exposes individuals to feared situations or objects in a controlled manner to reduce avoidance behaviors.
- Mindfulness-Based Therapies: Techniques that focus on mindfulness and relaxation to help individuals manage anxiety symptoms.
By addressing both the psychological and physiological aspects of anxiety, individuals can achieve better management of their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life. If anxiety is affecting your daily life, consider scheduling with us today!
Contact me today for your free consultation.
